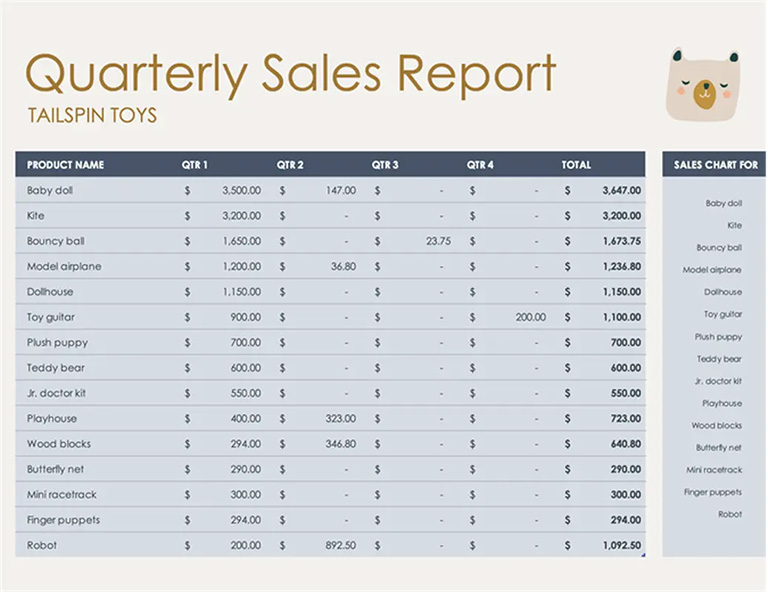
How create a sales report: types, templates and tips
Sales are the heart of any successful business, and improving your sales and marketing strategies is one of the simplest ways to increase profits. But to make smart, informed decisions about your customers and operations, you need reliable data.

That’s where sales reports come in. Sales reports are powerful tools that help you track performance, spot trends, and drive growth. Whether you’re a seasoned sales manager or a small business owner, knowing how to create and use these reports is essential.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through: what a sales report is, how to create one using our online presentation maker, the different types of reports you can use, and where to find ready-made templates to get started fast.
What is a sales report?
A sales report is a document that shows how many goods or services a company has sold during a specific period, such as a day, week, or month. It provides a clear snapshot of business performance and helps teams make informed decisions.
Key information included in a sales report ⤵
- Total revenue – The overall income generated from sales.
- Number of units sold – How many items or services were purchased.
- Average purchase value – The typical amount spent by each customer.
- Planning efficiency – A comparison of actual results vs. sales goals or forecasts.
A sales report presents data and helps the company analyze and interpret details such as:
- Sales trends – Analyze whether sales are increasing, decreasing, or remaining stable over time.
- Sales performance – Assess whether the company is meeting its sales targets or if the forecasts were overly optimistic or failed to account for key factors.
- Profitability – Identifies which products or services are generating the highest revenue and which ones are less profitable.
- Customer segmentation – Determine where the company achieves the highest sales—whether in specific regions, through online channels, or among certain types of customers.
- Recommendations – Conclusions and actionable recommendations for the company—such as which clients or partners to contact, where to allocate investments, and what adjustments to make to its product or service offering.
Types of sales report
Sales reports come in various forms, each tailored to address specific sales-related questions. Below are some of the most common types of sales reports, along with what they reveal, why they are important, and when to use them:
1. Sales report over time
These reports track changes in sales across a defined time period, helping to uncover trends and pinpoint which days, weeks, or months performed above or below expectations.
- Daily sales report
This report shows each day’s results, including total sales, number of transactions, and new customers. In many companies, salespeople enter their data into a system that creates the report automatically. Daily tracking is useful in fast-moving industries like retail or hospitality, where quick decisions are needed. - Weekly/monthly sales report
A summary of weekly or monthly sales helps identify patterns (e.g., “Sales are down every third week”) and possible causes – perhaps freelancing customers are waiting to be paid? These reports offer a broader view than daily reports and are useful for medium-term adjustments. - Quarterly/annual sales report
These reports show how sales match long-term goals, like annual revenue targets. They also highlight seasonal trends, such as a spike in holiday sales (“Christmas sales doubled compared to other months”). They’re useful for strategic planning and forecasting.
2. Sales performance report
This report shows how well individuals, teams, or products are doing compared to their goals—like revenue or units sold. It helps spot who’s doing great and who might need help. In large companies, managers often use it to compare salespeople’s results at the end of the month.
3. Sales pipeline report
This report shows what stage each customer is at—from showing interest to making a purchase. It helps you see future sales and find problems, like people not finishing their order or getting stuck in the negotiation stage.
4. Sales activity report
This report tracks what your salespeople are doing—such as the number of calls made, emails sent, or meetings held. It can show individual or team activity levels, helping managers assess productivity and identify who may need help (e.g., “Kevin made 50 calls but closed only 2 deals”).
5. Sales conversion report
This report shows how many leads become real sales. It helps find problems in the sales process—for example, if only 10% of visitors buy something. It’s useful for making each step of the customer journey better.
6. Sales forecast report
This report estimates future sales based on past performance and current activity. It’s essential for planning inventory, budgeting, and staffing. For example, if last December saw a sudden rise in demand, the forecast can guide how much stock to prepare for this year.
7. Product sales report
This report shows which products or services sell well and which don’t. It helps you decide what to restock, promote, or stop selling. For example, if thrillers sell more than romance books, you might order more thrillers.
8. Sales by region report
This report compares sales in different places, like cities or countries. It helps managers decide where to give more support—for example, if sales are low in one area, they can take action to improve it.
9. Sales growth report
This shows how much your sales have increased or decreased over time (e.g., month-over-month or year-over-year). It provides a clear picture of developments and overall performance trends.
How to create a sales report in a few steps?
Step 1: Know the purpose and your audience
Start by asking why you’re making the report and who will read it. This helps you decide what information to include.
- Executives – Want a big-picture view—key numbers and trends.
- Sales managers – Need detailed data on team and individual performance.
- Sales teams – Look for specific info about their own results and what’s working in the sales process.
Step 2: Carefully collect the data you need
Now that you know your goal and target audience, gather the data you need. You can get it from:
- CRM systems – for customer info, sales history, and deal status.
- Spreadsheets (e.g. Excel, Google Sheets) – for extra notes or data not in your CRM.
- Website analytics tools (such as Google Analytics) – to see how visitors find and use your site.
Step 3: Analyze the data
Now that you have the data, it’s time to make sense of it.
-
Check your goals – Did you hit your sales targets? If not, by how much?
-
Spot trends – Are sales rising, falling, or staying the same? Are there patterns or seasonal changes?
-
Use key metrics – Total sales, units sold, average order value (AOV), conversion rate, customer acquisition cost (CAC), Lifetime value (LTV), gross margin and lead sources.
-
Break down the data – Look at results by region, product, customer type, or marketing channel to find what’s working best.

Step 4: Show your data with visuals
Use charts and tables to make your data easy to understand. For example bar charts for comparing values or line charts to show changes over time. Keep it simple so readers can quickly see the key points.
Step 5: Summarize and recommend actions
Do not just show what happened-explain why it happened and what to do next. What are the main takeaways? What steps should the team take ? Write your conclusions and suggestions clearly and briefly.
Step 6: Export the report as a PDF
Exporting your report as a PDF keeps the format the same on all devices. It also helps protect the content from being changed.
Step 7: Turn Your PDF into an interactive flipbook with Publuu
With Publuu, you can turn your PDF into an interactive flipbook. This makes your report more modern and engaging:
- Realistic page – flip effect
Your report looks and feels like a real book, with smooth, animated flipping between pages. - Interactive elements
Add clickable hotspots with links, videos, image galleries to make your report more engaging and informative. - Easy sharing options
Share your flipbook with a link, embed it on your website, or send it by email. - Analytics and tracking
See who opened your report, how long they viewed it, and which pages they interacted with most. Perfect for tracking interest and engagement. - Polished, professional look
Publuu flipbooks feature a clean, modern design that gives your report a high-quality, professional finish.
MAKE YOUR OWN
Once your flipbook is ready, it’s time to share it. With Publuu, you can send a direct link, embed it on your website, generate a QR code for quick mobile access. Whether you’re presenting in a meeting or emailing it to clients, your report will look clear, impressive, and well-organized.
Tips for creating an effective sales report
1. Establish a regular reporting schedule
Decide how often to create reports – daily, weekly, monthly, or quarterly. Setting a routine (like daily reports each evening or monthly summaries every first Monday) helps keep your reporting process clear and consistent.
2. Use automation to save time
Tools like CRM systems and spreadsheets (e.g., Excel or Google Sheets) can generate reports automatically. For example, a report can be created every Friday at 4 p.m. with the latest transactions included –reducing errors and saving you time.
3. Gather feedback from report users
Talk to the people who use your reports. Ask if the data is helpful, what’s missing, and how it could be improved. Use their feedback to refine and improve your reports over time.
4. Experiment with different formats and visualizations
Experiment with charts, graphs, tables, or info graphics. People absorb information in different ways, so try out a few formats until you find what works best for your team or audience.
5. Keep it simple and focus on key information
Only include the most important data. Don’t overload the report with too many numbers. For example, show the top 5 best-selling and worst-performing products instead of listing all 20.
6. Maintain consistency in data presentation
Use the same style, layout, fonts, and colors each time. Consistency makes reports easier to read and compare. For example, always use green for revenue and red for losses.
7. Tailor the level of detail to your audience
Tailor the report based on who will read it. Sales teams might need detailed figures, while managers may prefer a short summary with key insights. Consider adding an executive summary for higher-level readers.
8. Include actionable insights
Don’t just present numbers – help your audience understand what to do with them. End your report with key findings, suggestions, possible next steps, or questions to drive action.
Sales report templates
Minimalist sales report template
Minimalist and eye-catching. This bold orange and black design makes your sales presentation stand out.
Maroon and red modern sales report template
A stylish template featuring rich maroon colors—perfect for professional presentations in business or corporate environments.
Modern sales report template
Modern and abstract design with bold fonts and shapes—great for delivering data in a creative, engaging way.
Quarter sales report template
A sharp and professional layout that’s great for breaking down quarterly results. Clean lines and modern fonts help keep your data easy to follow.
Monthly sales report template
Neat and simple—this layout works well for tracking monthly goals and performance. Easy to customize for quick updates and team check-ins.
Simple sales report template
Minimalist and elegant, this white and tosca-themed template offers a clean aesthetic. Ideal for straightforward presentations, it ensures your sales data remains the focal point.
Quarterly sales report template
Built-in visualizations help you track product performance and analyze quarterly sales results with ease.
Example of sales report
See how reports looks in Publuu’s interactive flipbook format. Ideal for sharing reports online with a realistic page-turn effect and professional digital presentation.
FAQ about sales reports
How do I write a sales report?
To create an effective sales report, follow these key steps:
Know your audience – Think about who will read the report and what they need to know.
Collect and summarize data – Include not only total sales but also metrics like average order value and customer acquisition cost.
Visualize your data – Use charts and tables to present information clearly.
Share as a flipbook – Use Publuu to turn your report into an interactive flipbook that’s easy to view and share online.
What are the key elements of a sales report?
A strong sales report should include a clear summary of the sales results achieved during the reporting period. It should also compare those results to the set goals or targets to show performance. Finally, it must present key findings, important observations, and specific recommendations for future actions.
How often is a sales report created?
This usually depends on what the organisation needs. For example:
- Daily – Brief summaries can be generated for sales teams.
- Monthly/quarterly – Detailed summaries for executives.
Who creates sales reports?
Sales reports can be created by:
- Sales managers – For tracking team performance.
- Sales analysts – For in-depth analysis and forecasting.
- CRM software – Many tools can generate and export reports automatically.
Conclusion on sales reports
Regular sales reporting is essential for growth and improvement. Whether you’re preparing a full report for management or a quick summary for your team, clarity is key. With Publuu, you can turn static PDFs into interactive flipbooks—making your sales reports more engaging and easy to share. It’s a great way to present your work with style and impact.
You might be also interested in:
10 Best Sales Presentations to Inspire your Sales Deck
What is a Sales Pitch and How to Craft One That Converts?